
Hydraulic excavators generally use a single row 4-point contact ball type inner tooth slewing support. In the operation of excavators, the slewing bearing bears complex loads such as axial force, radial force, and overturning torque, and its reasonable maintenance is very important. The maintenance and upkeep of the slewing bearing mainly includes lubrication and cleaning of the raceway and inner gear ring, maintenance of the inner and outer oil seals, and maintenance of the fastening bolts. We will provide specific explanations from 7 aspects.
1、Lubrication of the raceway

The rolling element and raceway of the slewing bearing are prone to damage and failure, with a high failure rate. During the use of excavators, adding lubricating grease to the raceway can reduce friction and wear between the rolling element, raceway, and isolation block. The space in the raceway cavity is narrow, and the resistance to adding lubricating grease is high, so manual grease guns need to be used for manual filling. The lubrication nozzles of the slewing bearing raceway are generally distributed on the outer circular wall of the slewing bearing, as shown in Figure 1.
The raceway cavity is generally lubricated with 2 # lithium based grease, and the lubrication cycle is generally 100 hours. In special working conditions such as high dust, high temperature, and continuous operation, the lubrication cycle should be appropriately shortened. When adding lubricating grease, it is necessary to rotate the slewing bearing approximately once every 15 ° to 25 ° rotation. When filling, attention should be paid to observing the outer sealing ring of the slewing bearing. When lubricating grease is seen to seep out from all around the outer sealing ring, the filling should be stopped.
When adding lubricating grease to the raceway cavity, it is necessary to avoid poor filling methods such as "static state refueling" and "single point refueling". This is because these poor filling methods can cause local oil leakage in the slewing bearing, and even permanent damage to the oil seal of the slewing bearing, leading to grease loss, invasion of impurities, and accelerated wear of the raceway. Be careful not to mix different types of lubricating greases to avoid premature failure. When replacing severely deteriorated lubricating grease in the raceway of the slewing bearing, the slewing bearing should be slowly and uniformly rotated while filling to ensure that the lubricating grease is evenly filled in the raceway. This process cannot be carried out too quickly, and it needs to be gradual in order to complete the metabolism of lubricating grease.
2.Maintenance of gear meshing area
Open the metal cover on the base of the rotary platform to observe the lubrication and wear of the inner gear ring of the rotary support and the small gear of the rotary motor reducer, as shown in Figure 2. The metal cover should be padded with rubber pads and fastened with bolts. If the bolts become loose or the rubber pad fails, water will seep into the lubrication chamber (oil collection plate) of the rotating inner gear ring from the metal cover, causing premature failure of the lubricating grease and a decrease in lubrication effect, leading to increased wear and corrosion of the gears.

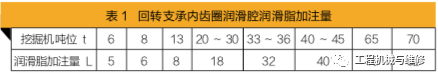
The method for replacing the lubricating grease in the inner gear ring lubrication chamber is as follows: first, use the working device to support the excavator, and the operator enters under the excavator track frame to open the metal cover (see Figure 3); Secondly, drop the excavator to the ground and start the excavator to perform a rotation action of about 10 turns to completely drain the ineffective lubricating grease. The lubrication chamber of the inner gear ring of the slewing bearing is also filled with 2 # lithium based grease, with a replacement cycle of generally 2000 hours. The amount of filling should be determined based on the excavator model, as shown in Table 1.

3.Maintenance of inner and outer oil seals
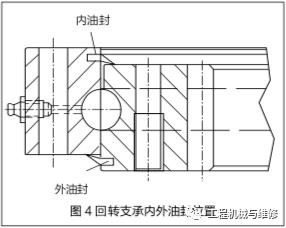
The inner and outer oil seals of the slewing bearing are of rubber sealing strip structure, which bears less pressure. The outer oil seal is located on the lower surface of the inner gear ring of the slewing bearing to prevent foreign objects such as sand particles from entering the raceway, causing wear of the rolling element and raceway; The inner oil seal is located on the upper surface of the outer circle of the slewing bearing to prevent the grease in the lubrication chamber of the inner gear ring from entering the raceway cavity. The positions of the inner and outer oil seals of the slewing bearing are shown in Figure 4
During the use of excavators, the inner and outer oil seals of the slewing bearing should be regularly checked for integrity. If damaged, they should be promptly repaired or replaced. If the sealing ring of the rotary motor reducer is damaged, it will cause the gear oil inside the reducer to leak into the lubrication chamber of the inner gear ring. During the meshing process between the inner gear ring of the rotary support and the small gear of the rotary motor reducer, the lubricating grease will mix with the gear oil, and the temperature will increase, causing the grease to become thinner. The thinner grease will be pushed to the upper end face of the inner gear ring and seep into the raceway through the inner oil seal, causing the outer oil seal to leak and drip, resulting in the rolling element The raceway and outer oil seal are damaged due to acceleration.
Some operators believe that the lubrication cycle of the slewing bearing is the same as that of the boom and stick, and that lubricating grease needs to be added every day. In fact, this is not correct. This is because adding lubricating grease too frequently can cause an excessive amount of grease in the raceway, which can lead to the leakage of grease at the inner and outer oil seals. At the same time, impurities will enter the interior of the slewing bearing raceway, accelerating the wear of the rolling element and raceway.
4.Maintenance of fastening bolts
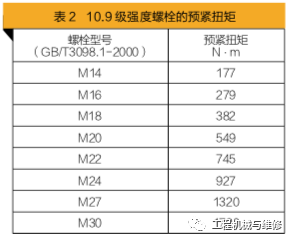
Some operators believe that the greater the force applied when tightening the bolts of the slewing bearing, the better. In fact, when the tensile force borne by the bolts exceeds the tensile strength of the bolts themselves, the pre tightening force cannot be formed. To ensure the reliability of bolt work, tightening should be carried out in accordance with the pre tightening torque regulations for this type of bolt. When selecting bolts with a strength of 10.9, flat washers made of 45 # steel, quenched and tempered at medium temperature, and with a hardness of HRC39 should be used. The use of spring washers is prohibited. The pre tightening torque of 10.9 grade strength bolts is shown in Table2
If 10% of the bolts in the slewing bearing become loose, the remaining bolts will bear greater force under tensile and compressive loads. Loose bolts can generate axial impact loads, exacerbating loosening and causing more bolt loosening, leading to bolt breakage and even machine damage and fatalities. Therefore, after the first 100h and 500h of operation of the slewing bearing, the pre tightening torque of the bolts should be checked. Afterwards, the pre tightening torque should be checked once every 1000 hours of operation to ensure that the bolts have sufficient pre tightening force.
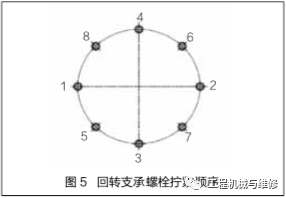
After repeated use, the tensile strength of the bolt will decrease. Although the torque during reinstallation meets the specified value, the pre tightening force of the tightened bolt will also decrease. Therefore, when tightening the bolts again, the torque should be 30~50N · m higher than the specified value. The tightening sequence of the slewing bearing bolts should be tightened multiple times in a 180 ° symmetrical direction, and the last tightening should ensure that all bolts have the same pre tightening force. The tightening sequence of the swing bearing bolts is shown in Figure 5.
5.Adjustment of gear clearance
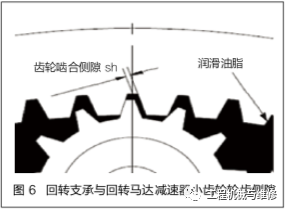
When assembling the inner gear ring of the slewing bearing and the output gear of the slewing motor reducer, the gear backlash should be adjusted at the highest point of the radial runout of the inner tooth circle of the slewing bearing. The meshing backlash is selected based on the size of the gear module. Under normal circumstances, the meshing backlash of the gear increases correspondingly with the increase of the gear teeth. At the point where the maximum radial runout of the inner tooth circle of the excavator slewing support occurs, the clearance Sh value between the tooth side of the slewing motor reducer gear is ≥ 0.03m (m is the gear modulus), as shown in Figure 6.
When adjusting the gear clearance, attention should be paid to observing whether the connecting bolts between the rotary motor reducer and the rotary platform are loose to avoid excessive or small gear meshing clearance. This is because if the clearance is too large, it will cause a greater impact on the gears during the start and stop of the excavator, which is prone to abnormal noise; If the clearance is too small, it can cause the swing bearing and the small gear of the swing motor reducer to get stuck, and even cause tooth breakage. The backlash between the gear teeth of the slewing bearing and the slewing motor reducer is shown in Figure 6.
When adjusting, attention should also be paid to observing whether the positioning pin between the rotary motor and the rotary platform is loose. The positioning pin and the pin hole belong to an interference fit. The positioning pin not only plays a positioning role, but also increases the tightening strength of the bolt of the rotary motor reducer and reduces the possibility of loosening the rotary motor reducer. The fixing bolts and positioning pins of the rotary motor are shown in Figure 7.

6.Maintenance of plug
The plug of the slewing bearing is set for dismantling the rolling element. The positioning pin is a conical structure used to fix blockages and prevent plugs from moving in series. The plug is located at the non load-bearing area of the slewing bearing, on both sides of the main load plane, as shown in Figure 8.
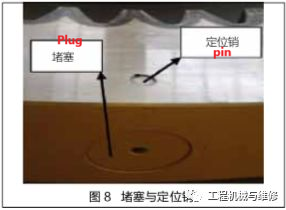
Once the positioning pin that fixes the plug becomes loose, it will cause plug displacement, causing changes in the raceway at the blocked area. When the rolling element moves, it will collide with the plug and make abnormal noises. When using an excavator, the operator should pay attention to clearing the soil covered by the plug and observe whether the plug has shifted.
7.Do not use water to flush the slewing bearing
It is prohibited to use water to wash the slewing bearing to prevent water, impurities, and dust from entering the slewing bearing raceway, causing corrosion and rusting of the raceway, resulting in the dilution of lubricating grease, damage to the lubrication state, and deterioration and failure of the lubricating grease; Avoid any solvent coming into contact with the rotary bearing oil seal to avoid corrosion of the oil seal.
In short, after using the excavator for a period of time, its slewing bearing is prone to noise, impact and other faults. The operator should pay attention to observation and timely inspection in order to eliminate the faults. Only by correctly and reasonably maintaining the slewing bearing can it ensure its normal operation, fully utilize its performance, and extend its service life.
Name: Ms Linda Ren
Tel:0086 15366795302
Whatsapp:008615366795302
Email:info@dpmachinery.com
Add:17th floor No.10 building, Tianfu Square,Tongshan district Xuzhou, Jiangsu Province, China--221000